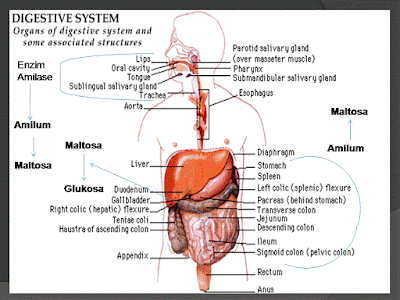
Metabolism is the term used to
describe the interconversion of chemical compounds in the body, the pathways
taken by individual molecules, their interrelationships, and the mechanisms
that regulate the flow of metabolites through the pathways. Metabolic pathways
fall into three categories.
(1) Anabolic pathways, which are those involved in the synthesis of larger and more complex compounds from smaller precursors—for example, the synthesis of protein from amino acids and the synthesis of reserves of triacylglycerol and glycogen. Anabolic pathways are endothermic.
(2) Catabolic pathways, which are involved in the breakdown of larger molecules, commonly involving oxidative reactions; they are exothermic, producing reducing equivalents, and, mainly via the respiratory chain , ATP.
(3) Amphibolic pathways, which occur at the “crossroads” of metabolism, acting as links between the anabolic and catabolic pathways, for example, the citric acid cycle.
(1) Anabolic pathways, which are those involved in the synthesis of larger and more complex compounds from smaller precursors—for example, the synthesis of protein from amino acids and the synthesis of reserves of triacylglycerol and glycogen. Anabolic pathways are endothermic.
(2) Catabolic pathways, which are involved in the breakdown of larger molecules, commonly involving oxidative reactions; they are exothermic, producing reducing equivalents, and, mainly via the respiratory chain , ATP.
(3) Amphibolic pathways, which occur at the “crossroads” of metabolism, acting as links between the anabolic and catabolic pathways, for example, the citric acid cycle.